
Degreasing, Educational, Simple Science
Blurred Lines: The Murky World of Cleaners and Degreasers
Do you have trouble making a clear distinction between a cleaner and a degreaser? Or wonder if there even is a distinction? If so, you’re not alone. Various products may be labeled as an all-purpose cleaner, a degreaser, or a cleaner-degreaser. So what’s a cleaning professional to think?
Both cleaners and degreasers have their place in a maintenance arsenal. Knowing when to reach for what will help make your cleaning job easier while keeping your facility safe and grime free.

Degreaser Defined
It’s murky territory between cleaners and degreasers. In the industrial and institutional cleaning world, a degreaser is defined simply as a chemical product that removes grease. However some all-purpose cleaners may also remove some grease. Degreasers are a subset of cleaners, so all degreasers are cleaners but not all cleaners are degreasers.
Still a bit blurry? Additional explanation may help clear things up.
The Simple Science of Degreasers
Cleaning chemicals are formulated to be acidic, alkaline (basic) or neutral. These designations are determined by a solution’s pH (concentration of the hydrogen ion) level, and range from 0 to 14 on the pH scale (see graphic below). A lower pH number means a solution is more acidic, while a higher pH number indicates it is more alkaline. Solutions that land in the middle around 7 are considered neutral.
Grease is an organic soil, meaning it comes from something living. Organic soils – especially tough commercial kitchen messes – are best removed with alkaline solutions since higher pH levels can more easily break down fats, oils and proteins typically found in kitchens. The more “caked-on” a grease is, the more heavy-duty or higher alkaline cleaner you will need. At the extreme end, oven cleaners are highly alkaline because they need to remove caked-on carbonized soil.
Degreasers often also contain other ingredients like a petroleum-based solvent or a natural solvent like citrus to further aid in breaking down grease. Nyco’s Citra Blaze 535, for example, is a degreaser formulated with a citrus solvent. It cuts through heavy buildups of grease and caked-on food soils quickly.
The Purpose of All-Purpose Cleaners
All-purpose cleaners are pH neutral between 6 and 8 on the pH scale. They are best suited for cleaning surfaces that are dusty or lightly soiled, or that require a general (non-greasy) cleaning. While degreasers can effectively clean non-greasy surfaces, they are “more than you need” for this type of cleaning. In general, all-purpose neutral cleaners are safer for people and surfaces.
The Cleaner-Degreaser Continuum
Some manufacturers, including Nyco, label certain products as “cleaner-degreasers.” These products reside in the in-between land – more effective on greasy soils than an all-purpose cleaner yet closer to neutral pH and safer than a heavy-duty degreaser. Think of cleaners and degreasers as falling on a “cleaner-degreaser continuum” that parallels the upper half of the pH scale: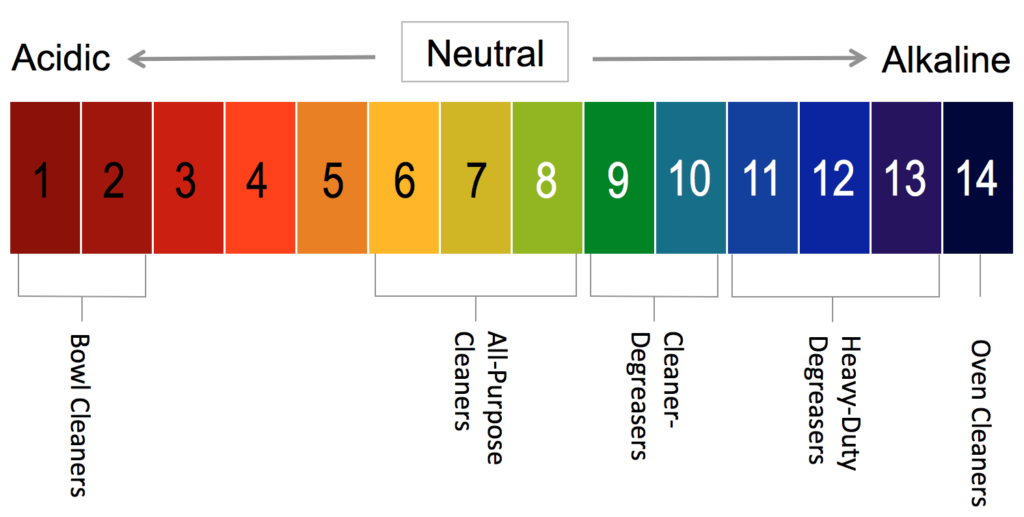
When to Use a Cleaner or Degreaser
These are the questions to ask when choosing your cleaner for a specific job:
1. What is the type of soil to be cleaned?
Degreasers are designed to break up grease for easy removal. However, they are often more abrasive than a typical all-purpose cleaner. Heavily soiled areas that cannot be cleaned with an all-purpose cleaner call for a degreaser. Nyco’s Blaze 8 is a powerful and fast-acting degreaser that cuts through heavy buildups of grease and other soil.
2. What is the surface/substrate that needs cleaning?
Certain surfaces like plastic, glass, metal or painted wood may be better served with an all-purpose or multi-surface cleaner with a neutral pH. Try OM1 Series Multi-Surface Cleaner for a ready-to-use multi-purpose cleaner that has universal applications and is non-corrosive.
3. What is the application/type of equipment that needs cleaning?
Large or heavy equipment that can’t be moved may benefit from a foaming degreaser for longer contact time. A foaming degreaser like Blaze 5T is ideal for use on vertical surfaces and equipment where increased cleaning contact time is needed.
4. What safety issues need to be considered?
Floors are one area where safety considerations are a top priority. Degreasers used on floors should be formulated with high-traction properties to reduce the incidence of slip-and-fall accidents. Environmental safety—both in use and disposal—should be taken into account as well. Always follow the manufacturer’s directions when using any product.
Types of Degreasers
| Degreaser | pH Range | Chemical Properties | Main Applications |
| General Purpose Cleaner-Degreaser | Mildly alkaline | Contains solvent, detergent, and alkaline builders |
|
| “Green” Degreaser | Neutral to mildly alkaline | Surfactant based, may use ‘green’ water-soluble solvent |
|
| RTU Degreaser | Variable, based on the soil levels and surfaces | Surfactants, water- soluble solvent and alkaline builders |
|
| Floor Degreaser | Variable | Low foaming surfactants with water-soluble solvent and variable alkaline builders |
|
| Industrial Degreaser | More alkaline | Contains higher levels of water-soluble solvent, combined with detergent and more alkalinity |
|
| Oven Degreaser | Highly Alkaline | High foaming surfactants, alkaline builders, may contain water- soluble solvent |
|
Having the right cleaning chemicals for the job and the knowledge of when to use them will help you clean quickly and effectively while maintaining a safer facility.
Simple Science Degreaser Vocabulary
- pH level – A measure from 0 – 14 of the acidity or alkalinity of water-soluble substances.
- Neutral – 7 on the pH scale, making it neither acidic nor alkaline. Cleaners are considered neutral when they are between 6 and 8 on the pH scale.
- Alkaline – Above 7 on the pH scale; the opposite of acidic.
- Solvent – A liquid capable of dissolving other substances.
- Organic soil – Soil originating from living matter, such as blood, urine, grease, and food.
- Inorganic soil – Soil not originating from living matter, such as mud, dirt, or sand.
